Have you ever stopped to wonder what happens when two seemingly distinct colors, like a calm blue and a lively green, come together? It’s a rather interesting thought, because these two shades, while close on a color wheel, actually hold different places in the world of color theory. People often ask about this mix, expecting just one simple answer, but the truth is, it’s a bit more involved than that, depending on how you’re doing the mixing.
You see, blue is what we call a primary color, something that can’t be made by combining other colors. Green, on the other hand, is a secondary color, meaning it’s already a blend of two primaries – blue and yellow, as a matter of fact. So, when you bring blue and green together, you’re not just mixing two random colors; you’re combining a foundational shade with a color that already has a piece of blue within it. This makes the outcome quite varied, depending on the exact shades you choose to combine.
The result of this mixing isn't always just one single color, which is interesting. Instead, you can get a whole range of beautiful, watery, or earthy tones. It really just depends on the exact proportions and the kind of materials you're working with, whether that's paint, light, or something else entirely. We’re going to explore all of that, so you can get a clearer picture of what happens when these two compelling colors meet.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Basics of Color Blending
What Does Blue and Green Make in Paint and Pigment?
Exploring the Spectrum - What Does Blue and Green Make When Subtractive?
How Does Light Mixing Change What Does Blue and Green Make?
The Feeling of Color - What Does Blue and Green Make Us Feel?
Cyan and Its Uses - What Does Blue and Green Make in Our World?
Blue and Green in the Natural World - What Does Blue and Green Make in Eyes?
Other Color Combinations - What Does Blue and Green Make When Mixed with Others?
Understanding the Basics of Color Blending
Before we get into the specifics of what happens when blue and green come together, it’s helpful to have a little background on how colors generally work. You see, colors are typically grouped into different families based on how they are created. There are primary colors, which are the fundamental building blocks, so to speak. Then, there are secondary colors, which come from mixing two primaries. And beyond that, you have tertiary colors, which are a mix of a primary and a secondary. It’s a bit like a family tree for colors, you know?
Blue, as we touched on earlier, is a primary color. This means you can’t make blue by mixing anything else. It just is. Green, however, is a secondary color. It’s born from the union of blue and yellow. This is pretty important because it means green already carries a bit of blue within its essence. The exact shade of green you have can also vary quite a bit, too, depending on whether it has more yellow or more blue pigment in it. This subtle difference in the green itself will actually affect the final shade you get when you mix it with more blue, as a matter of fact.
So, when you mix a primary color like blue with a secondary color like green, you’re stepping into a category of color mixing that creates something called a tertiary color. It’s not always just a simple combination; it’s a creation of a new, more nuanced shade. This blending process can lead to a whole range of interesting outcomes, and it really just shows how much variety there is in the world of color, apparently.
What Does Blue and Green Make in Paint and Pigment?
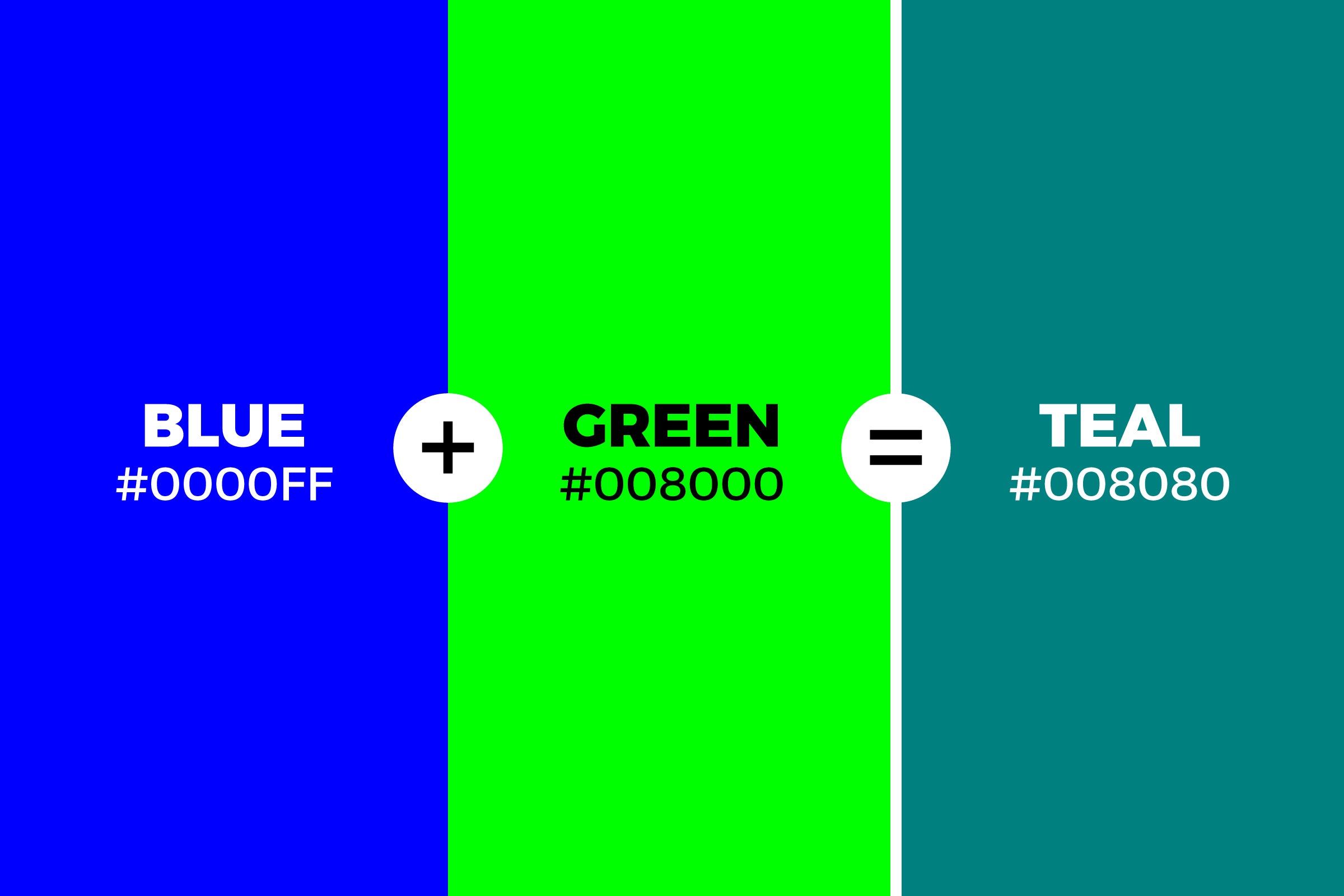
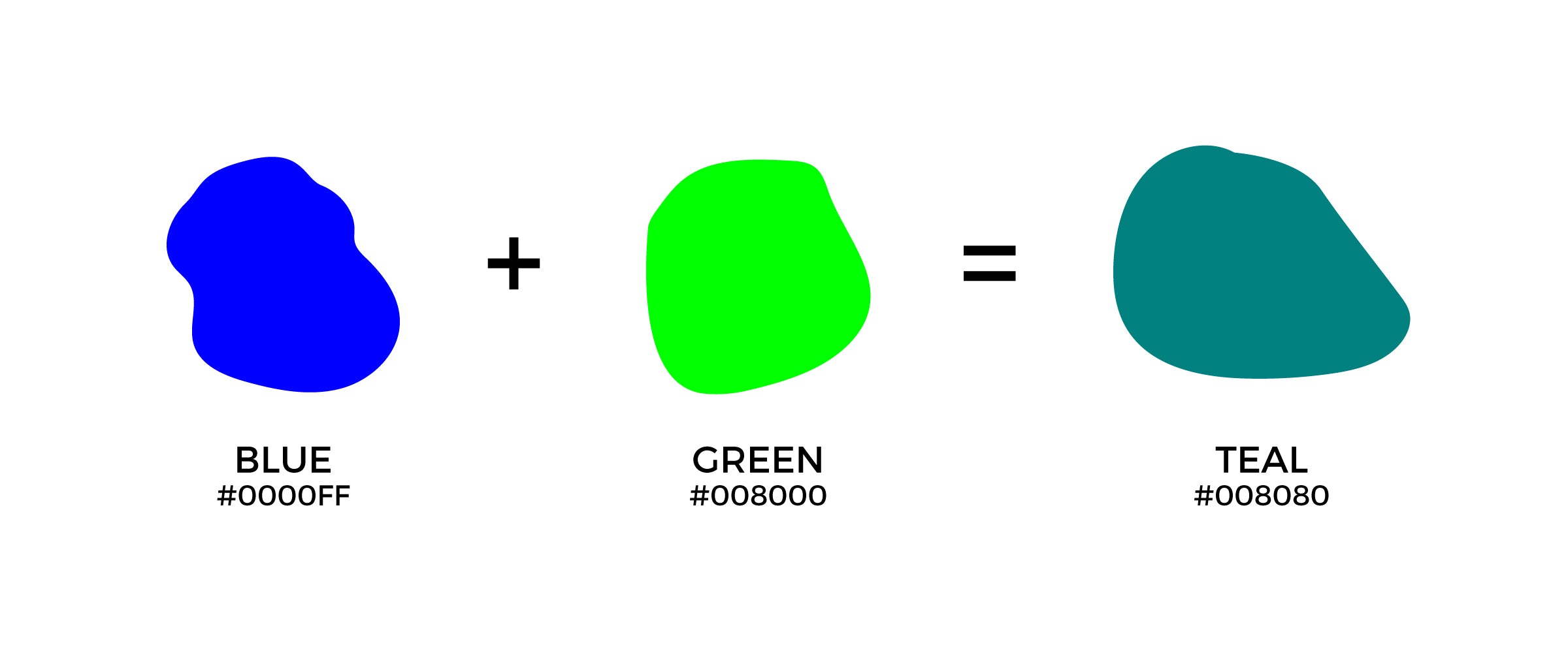
When you take paints or other physical pigments and combine blue and green, you are typically working within what’s known as the subtractive color model. This is the way colors work when light is absorbed and reflected, which is what happens with paints, crayons, or even the ink in your printer. So, what exactly does blue and green make when you’re holding a brush or crayon? Well, the most common outcome is a beautiful range of shades that remind you of the ocean or a deep forest. You know, like a teal or a turquoise color, depending on the exact amounts of each you use.
The specific green you choose really plays a big part in the final color. If your green has more yellow in it, the resulting mix might lean a little warmer, perhaps a bit more like a bright aqua. If your green is a cooler shade, with more blue already present, then the combined color will likely be a deeper, more profound teal. It’s almost like each green has its own personality, and that personality influences the final blended shade. This is why artists often have many different tubes of "green" paint, because they all behave a little differently when mixed.
It’s not just about getting one specific color, either. Mixing blue and green in this way allows for a spectrum of colors. Think of it like a gradient on a color wheel, where you move smoothly from a pure blue through various shades of blue-green until you reach a pure green. This means you can create a wide array of beautiful blues and greens that aren't quite one or the other, but something unique in between. It really does depend on the purpose you have in mind for these colors, you see.
Exploring the Spectrum - What Does Blue and Green Make When Subtractive?
So, when we talk about the subtractive color model, which is how paints and inks work, mixing blue and green doesn't just give you one single, fixed color. Instead, it creates a whole range of colors that fall somewhere between blue and green on the color wheel. This is a bit of an oversimplification, but it helps to think of it as a journey from one color to the other, with many stops along the way. You can make a very blue-heavy shade, a perfectly balanced one, or a very green-heavy shade, just by changing the proportions, basically.
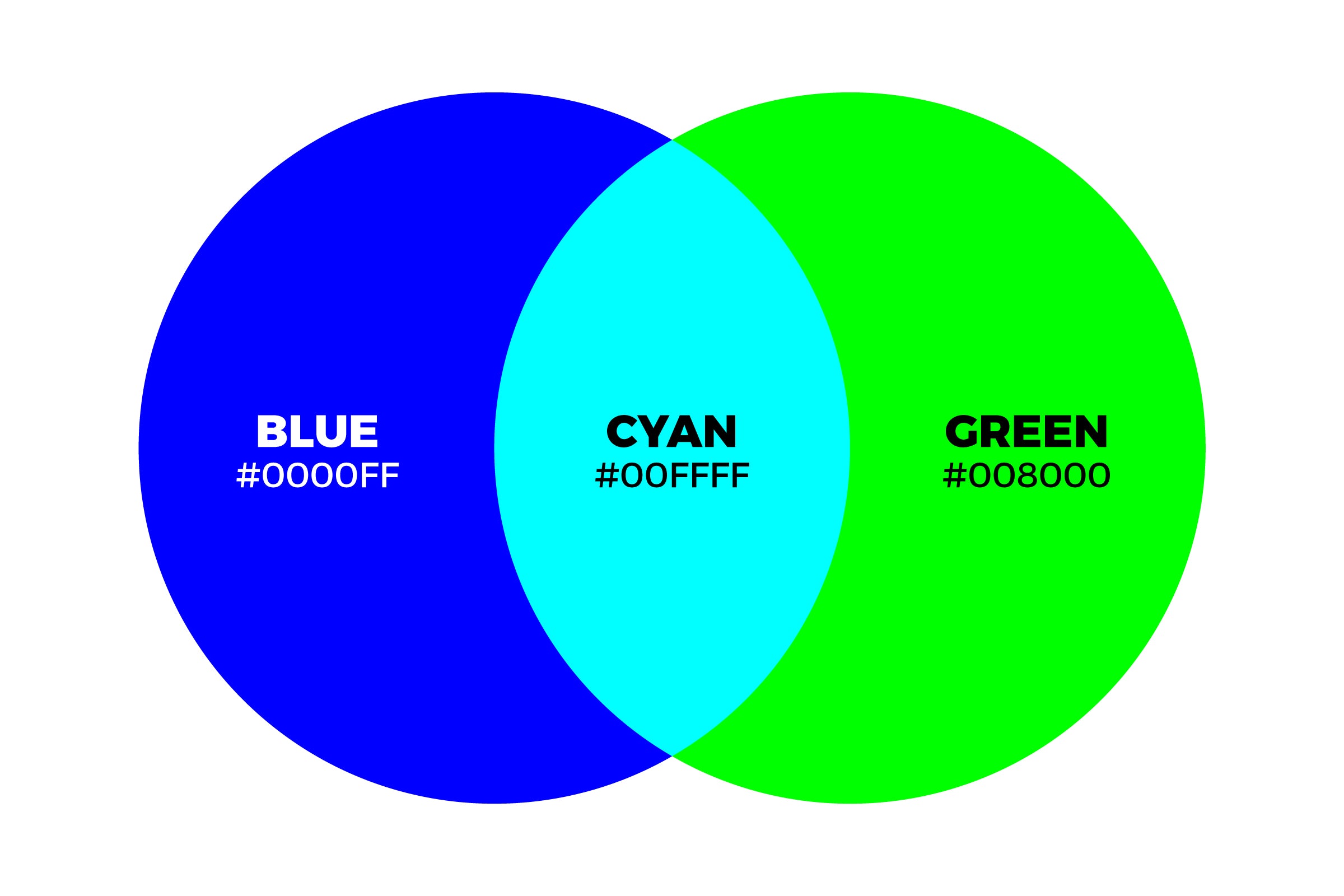
The most famous result of mixing blue and green pigments in roughly equal amounts is often a color known as cyan. This color is a secondary color on the CMYK color model, which is what printers use. Cyan is a cool color, a bright, greenish-blue that you often see in printing and digital displays. It’s a very distinct shade, and it really shows how a simple combination can lead to a very important color in many different systems, you know?
But beyond cyan, you can also create shades like aqua, which is typically a lighter, brighter blue-green, very reminiscent of clear water. Then there’s teal, which is usually a deeper, richer blue-green, sometimes with a hint of gray or brown, giving it a more sophisticated feel. The possibilities are quite varied, and it’s all about experimenting with the amounts of each color. It’s pretty amazing how much variety you can get from just two starting points, actually.
How Does Light Mixing Change What Does Blue and Green Make?
Now, let's switch gears a little and talk about light. When we mix colors of light, it works very differently from mixing paints. This is called additive color mixing, and it’s how screens like your television or computer monitor create all their colors. In this system, the primary colors are red, green, and blue – often called RGB. So, what does blue and green make when you’re talking about light?
When you combine blue light and green light, you also get cyan. This is the same cyan we talked about with pigments, but it’s created in a completely different way. With light, when you mix these two primary colors of light, you are adding wavelengths together, making the resulting color brighter. It’s like shining two flashlights with colored filters onto a wall; the spot where the blue and green light overlap will appear cyan. This is a very important concept in digital displays, as it helps create the full spectrum of colors we see on our screens, you know.
It’s important to remember that this is the opposite of how paints work. With paints, mixing colors makes them darker because they absorb more light. With light, mixing colors makes them brighter because they are emitting more light. In fact, if you mix red, green, and blue light together in equal amounts, you actually get white light. This is a pretty cool phenomenon, and it’s the foundation of how our digital world displays such a wide array of colors, basically.
The Feeling of Color - What Does Blue and Green Make Us Feel?
Colors aren't just about what they look like; they also have a big impact on how we feel. Blue, for example, is often associated with feelings of calm, peace, and stability. It can make you think of the sky or the ocean, bringing a sense of serenity. Green, on the other hand, is frequently linked to nature, growth, and freshness. It often brings a feeling of harmony and balance, you know, like a peaceful forest.
So, when you mix blue and green, the resulting shades often carry a blend of these feelings. Teal and aqua, for instance, often evoke a sense of tranquility and refreshment, much like looking at clear, calm water. They can be very soothing colors, perfect for spaces where you want to feel relaxed and at ease. This is why you often see these shades used in spas or bedrooms, because they really do help create a peaceful atmosphere, apparently.
The psychological effects of these combined colors are quite interesting. They can promote a sense of well-being and connection to the natural world. This is why designers often use blue-green tones to create spaces that feel both comforting and invigorating. The names themselves, like "seafoam" or "lagoon," often reflect these natural connections, reinforcing the calming and refreshing feelings they bring. It’s pretty neat how much impact a color can have on our mood, actually.
Cyan and Its Uses - What Does Blue and Green Make in Our World?
Cyan, which is a key result of mixing blue and green, plays a surprisingly big role in our daily lives, even if we don't always notice it. As we mentioned, it’s a secondary color in both the RGB (red, green, blue) color model for light and the CMYK (cyan, magenta, yellow, black) color model for printing. This means it’s fundamental to how we see colors on screens and how images are printed on paper, you know?
In printing, cyan ink is one of the four essential colors used to create a full range of hues. When your printer mixes cyan with magenta and yellow, it can produce almost any color imaginable. This is how magazines, brochures, and even your home photos get their vibrant looks. It’s a bit like magic, but it’s really just clever color science at work, basically.
Beyond printing and digital displays, cyan also appears quite a bit in nature. Think about the clear blue waters of a tropical ocean, or the color of certain minerals. It’s a very cool color, and its presence in both natural and manufactured settings shows just how versatile and important this blue-green mixture truly is. It’s a pretty compelling color, really, when you start to notice it more.
Blue and Green in the Natural World - What Does Blue and Green Make in Eyes?
The combination of blue and green isn't just something we create in art or on screens; it's also very much a part of the natural world around us. From the vastness of the sky and the deepness of the ocean to the lushness of forests and the delicate shades of leaves, these colors are everywhere. They often blend seamlessly, creating a sense of natural harmony. You know, like the way the shallow parts of the ocean can look a vibrant aqua, while deeper areas appear a darker blue or teal, depending on the light and depth.
Interestingly, these colors also play a part in human biology, specifically when it comes to eye color. People often wonder how eye colors like blue and green come about, and what happens when parents with different eye colors have children. It’s a complex area, but it’s fascinating how the genetics work out. For instance, you can absolutely have green eyes even if one parent has blue eyes and the other has brown. It's not a direct mix of pigments like paint, but rather how light interacts with the amount of melanin present in the iris, which is pretty cool.
So, while the question "what does blue and green make" might initially make you think of mixing paints, it also applies to understanding how these colors appear in the living world, including in our very own eyes. The way light scatters and reflects off the structures in the eye determines the perceived color, and it’s a very delicate balance that creates those beautiful blue and green shades we see in people, you know.
Other Color Combinations - What Does Blue and Green Make When Mixed with Others?
While our main focus has been on what happens when blue and green come together, it’s also worth a quick look at how these colors interact with others. This helps to show the broader picture of color mixing. For example, if you mix red and green pigments, you usually end up with a brown color. It’s not quite black, but a sort of earthy brown, and it really depends on how much of each color you use, you know.
In the additive light system, as we talked about, mixing red, green, and blue light together gives you white light. This is a very important concept in how screens work, creating the full spectrum of visible light from just three primary colors of light. It’s a powerful demonstration of how light colors combine to create lighter outcomes, completely unlike pigments, basically.
And what about more complex mixes? For instance, if you were to mix purple and green pigments, you’d typically get a light, cool brown. This happens because purple is made from red and blue, and green is made from yellow and blue. So, when you mix purple and green, you're essentially combining all three primary colors (red, yellow, blue) in various amounts, which tends to lead to a brownish shade. The exact outcome can be influenced by the dominant color, so if there's more blue, that will be the most recognizable undertone, you know?
Related Resources:
Detail Author:
- Name : Ms. Lacey Quigley DDS
- Username : sven.stamm
- Email : oren.howe@braun.org
- Birthdate : 1995-01-09
- Address : 91410 Schuster Key Apt. 203 Napoleonton, IN 89025-1279
- Phone : +1-765-988-1335
- Company : Kassulke, Swaniawski and Hermiston
- Job : Human Resources Assistant
- Bio : Doloribus sit officiis sed. Ipsam deleniti saepe ex illum. Ex incidunt facilis labore modi quibusdam aspernatur.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/kiannarobel
- username : kiannarobel
- bio : Ipsam nam qui voluptatem a accusamus nemo.
- followers : 1476
- following : 2760
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/kianna9996
- username : kianna9996
- bio : Occaecati quibusdam numquam ipsa dolores odit. Saepe recusandae porro facilis similique.
- followers : 2519
- following : 2687
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/kianna_robel
- username : kianna_robel
- bio : Harum nihil error et assumenda optio voluptate. Aut repellat voluptate id saepe blanditiis quas nemo vitae. Numquam quidem quod eligendi dolorem omnis est.
- followers : 4151
- following : 156